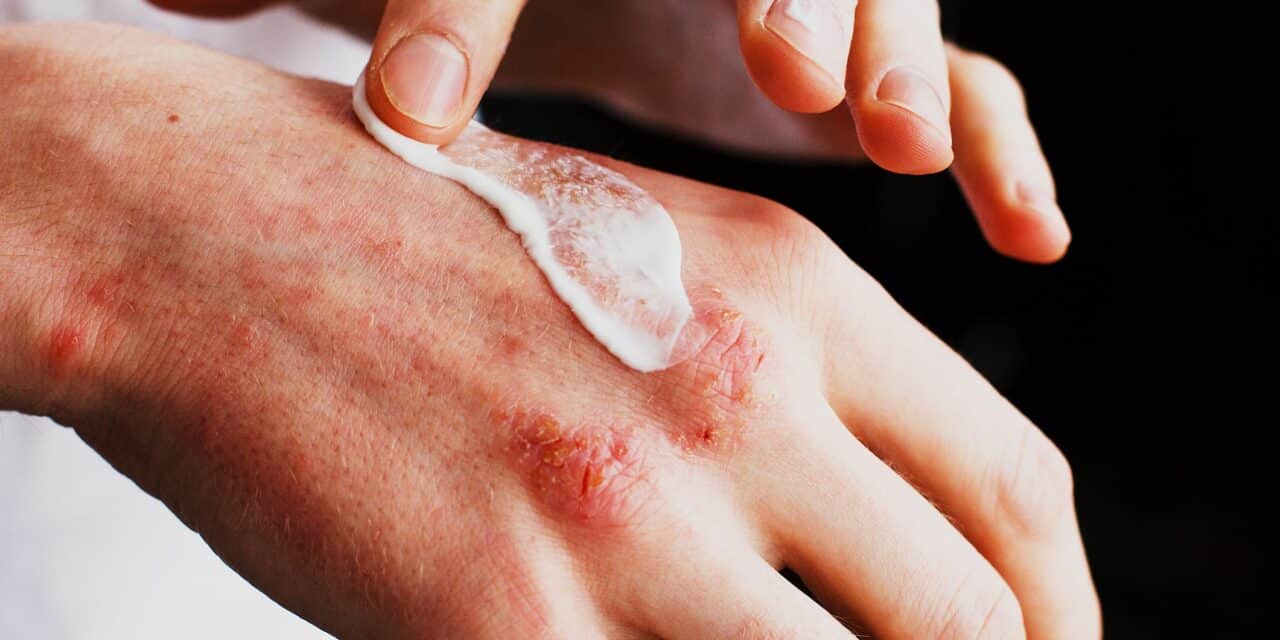
Late-breaking clinical trial data shows that a topical cream—currently under investigation in the US while approved in other markets—provides relief for patients with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema.
LEO Pharma, specializing in medical dermatology, presented late-breaking data at the American Academy of Dermatology (ADD) 2025 Annual Meeting showing that delgocitinib cream produced a deep, consistent, and sustained response in a subgroup of patients with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema.
The presentation marked the third consecutive year that LEO Pharma has presented late-breaking data at AAD. Alongside this presentation, new systemic exposure data also was shared for delgocitinib cream at the meeting.
“The data unveiled today further contributes to LEO Pharma’s ever-growing body of scientific evidence for the treatment of moderate to severe [chronic hand eczema],” says Christophe Bourdon, chief executive officer, LEO Pharma, in a release. “Our research and work in [chronic hand eczema] is a testament to our ambition to maintain the broadest global product portfolio in dermatology, and I am proud we can share this latest analysis from our pivotal DELTA trials.”
Delgocitinib cream is currently under investigation in the United States.
Late-Breaking Post Hoc Data Analysis
The subgroup analysis presented was based on the treatment response in patients with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema treated with delgocitinib cream for 16 weeks compared to patients treated with the cream vehicle in the DELTA 1 and DELTA 2 trials. The subgroup in this analysis was defined as patients with either a deep, consistent and/or maintained treatment response.
The findings from the post hoc analysis highlight that delgocitinib cream produced a strong treatment response across this subgroup of patients.
A deep response, defined as a Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), HESD pain 0/1, and/or a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score of 0/1 at week 16, was achieved by more patients receiving delgocitinib cream versus the cream vehicle. At Week 16, 30.0% vs 9.4% of patients achieved a HESD itch of 0/1, 35.2% vs 16.0% achieved HESD pain 0/1, and 33.3% vs 13.9% achieved a DLQI score of 0/1.
Greater percentages of patients receiving delgocitinib cream versus the cream vehicle over the trial period achieved a consistent response of at least a 4-point reduction from baseline in HESD itch (24.1% vs. 6.6%) or pain (25.0% vs. 9.0%) or at least 75% improvement on the Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI-75) (27.3% vs. 8.1%).
A maintained response was defined as achieving an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA)-CHE of 0 (clear) at week 16 and maintaining IGA-CHE 0 off treatment. Among patients receiving delgocitinib cream who achieved an IGA-CHE score of 0 at week 16, 32.9% maintained a score of 0 after 8 weeks and 15.7% after 16 weeks.
“It is so exciting to see such a strong response in a subgroup of patients treated with delgocitinib cream,” says April W Armstrong, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at the University of California-Los Angeles, in a release. “The results across the various treatment metrics are promising and demonstrate the future potential that delgocitinib cream may have in offering a new treatment option for those living with this unique and burdensome disease.”
Systemic Exposure Analysis
Alongside the late-breaker presentation, new systemic exposure data from the DELTA 2 trial were presented as an e-poster. The data was based on an investigation into the systemic exposure of twice-daily delgocitinib cream under high-use conditions in the phase 3 DELTA 2 trial in adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema.
Additionally, the systemic exposure from the DELTA 2 trial was compared with adult pharmacokinetics (PK) data from a phase 1 trial in patients with moderate to severe AD, and with oral administration using the lowest dose tested in an oral PK study in healthy adults.
The DELTA 1, 2 and 3 Trials
The primary objective for the randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multi-center phase 3 clinical trials (DELTA 1 and DELTA 2) was to evaluate the efficacy of twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream compared with the cream vehicle in the treatment of adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema.
The primary endpoint of the trials was the Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema treatment success (IGA-CHE TS) at week 16. Treatment success was defined as an IGA-CHE score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a two-step improvement from baseline. Additional IGA-CHE scores included 2 (mild), 3 (moderate), and 4 (severe).
Key secondary endpoints at week 16 included a reduction of itch and pain scores of ≥4 points measured by the Hand Eczema Symptom Diary from baseline to week 16, as well as at least 75% improvement from baseline and at least 90% improvement from baseline on the Hand Eczema Severity Index at week 16. The number of treatment-emergent adverse events from baseline to week 16 defined the key safety endpoint of the trials.
Subjects who completed 16 weeks of treatment with delgocitinib cream or the cream vehicle twice daily in trials DELTA 1 or DELTA 2 were offered to roll over to the 36-week DELTA 3 open-label, multi-site extension trial. The purpose of this extension trial was to evaluate the long-term safety of delgocitinib.
Delgocitinib Cream
Delgocitinib cream is currently under investigation in the United States and other markets. Delgocitinib cream is currently approved in the European Union, United Kingdom, Switzerland, and the United Arab Emirates under the brand name Anzupgo for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic hand eczema in adults for whom topical corticosteroids are inadequate or inappropriate.
Delgocitinib cream is a topical pan-Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic hand eczema. It inhibits the activation of JAK-STAT signaling, which plays a key role in the pathogenesis of chronic hand eczema. The pathophysiology is characterized by skin barrier dysfunction, inflammation of the skin, and alterations of the skin microbiome.
Chronic hand eczema is defined as hand eczema that lasts for more than three months or relapses twice or more within a year.
ID 140715842 © Olga Ternavskaia | Dreamstime.com